8.8 KiB
Accessing the Data Observatory
The workflow for accessing the Data Observatory includes using a SQL query to apply a specific method of data enrichment or analysis to your data. You can access the Data Observatory by applying a custom query in CARTO Builder, or directly through the SQL API.
Prerequisites
You must have an Enterprise account and be familiar with using SQL requests.
-
The Data Observatory catalog includes data that is managed by CARTO, on a SaaS cloud platform. For Enterprise users, the Data Observatory can be enabled by contacting CARTO.
-
A set of Data Observatory functions (prefaced with "OBS" for Observatory), allow you to retrieve boundaries and measures data through a SQL request. These functions should be used with UPDATE and INSERT statements, not SELECT statements, as we are currently not supporting dynamic use of the Data Observatory
Tip: See the recommended Best Practices for using the Data Observatory.
Enrich from Data Observatory
As an alternative to using SQL queries, you can apply the Enrich from Data Observatory ANALYSIS to a selected map layer in CARTO Builder. This enables you add a new column with contextual demographic and economic measures, without having to apply the code yourself. For details, see the Enrich from Data Observatory Guide in our Learn hub.
Apply OBS Functions to a Dataset
This procedure describes how to access the Data Observatory functions by applying SQL queries in a selected dataset.
-
Review the prerequisites section before attempting to access any of the Data Observatory functions
An overview for each of the analyzed functions of data appears, and indicates the unique function signature needed to access the catalog item. You can copy the OBS function from the Data Observatory catalog and modify the placeholder parameters shown in curly brackets (e.g. "{table_name}").
- From Your datasets dashboard in CARTO, click NEW DATASET and CREATE EMPTY DATASET.
This creates an untitled table. You can get population measurements from the Data Observatory to build your dataset and create a map.
-
The SQL view is available when you are viewing your dataset in table view (Data View). Click the slider to switch between viewing your data by METADATA (table) to SQL (opens the SQL view).
-
Apply the OBS function to modify your table.
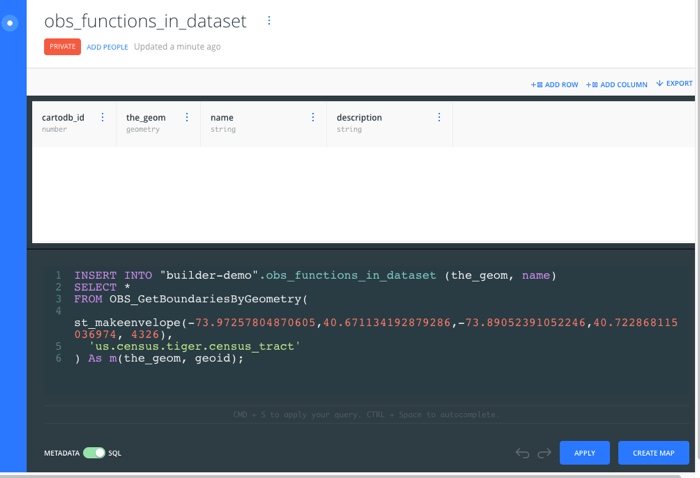
For example, the following image displays a SQL query using the Boundary function, OBS_GetBoundariesByGeometry(geom geometry, geometry_id text) function. The SQL query inserts the boundary data as a single polygon geometry for each row of data.
Tip: Want to insert population data to create a dataset? Replace {my table name} with your dataset name, and apply the SQL query:
INSERT INTO {my table name} (the_geom, name)
SELECT *
FROM OBS_GetBoundariesByGeometry(
st_makeenvelope(-73.97257804870605,40.671134192879286,-73.89052391052246,40.722868115036974, 4326),
'us.census.tiger.census_tract'
) As m(the_geom, geoid);
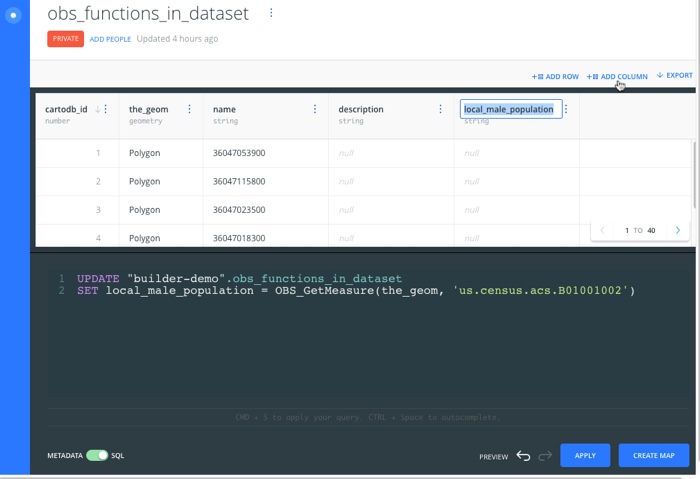
Another example shows how to get the local male population into your dataset. Before applying the SQL query, click ADD COLUMN to create and name a column to store the [OBS_GetMeasure]({{ site.dataobservatory_docs}}/reference/#obsgetmeasurepolygon-geometry-measureid-text) data.
Tip: Want to update your dataset to include the local male population from the Data Observatory? Replace {my table name} with your dataset name, and apply the SQL query:
UPDATE {my table name}
SET local_male_population = OBS_GetMeasure(the_geom, 'us.census.acs.B01001002')
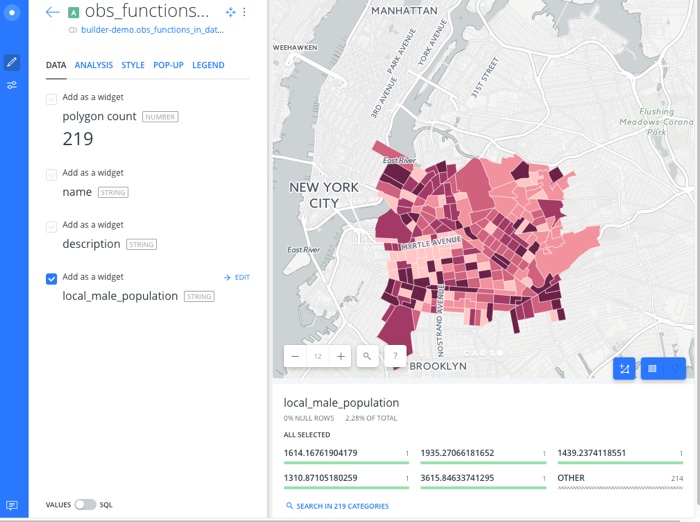
- Click CREATE MAP from your dataset, to visualize the Data Observatory results. You can add custom styling, and add widgets to better visualize your data
SQL API and OBS Functions
This procedure describes how to access the Data Observatory functions directly through the SQL API.
-
In order to use the SQL API, you must be [authenticated]({{ site.bdataobservatory_docs }}/guides/authentication/#authentication) using API keys
Note: Review the prerequisites section before attempting to access any of the Data Observatory functions and view the Data Observatory Catalog to identify the OBS function you are looking for.
-
Query the Data Observatory directly with a specified
OBSfunction to apply the results (Measures/Boundaries data) to your table, with the INSERT or UPDATE function
https://{username}.carto.com/api/v2/sql?q=UPDATE {tablename}
SET local_male_population = OBS_GetMeasure(the_geom, 'us.census.acs.B01001002')&api_key={api_key}
Tips
Other useful tips about OBS functions:
- Some Data Observatory functions return geometries, enabling you to apply an UPDATE statement with an OBS function, to update
the_geomcolumn - To include [water clipping levels]({{ site.dataobservatory_docs }}/guides/overview/#water-clipping-levels) as part of your results, append
_clippedas part of the OBS function. For example:
UPDATE {tablename}
SET local_male_population = OBS_GetMeasure(the_geom, 'us.census.acs.B01001002','area','us.census.tiger.census_tract_clipped')
Best Practices
The following usage notes are recommended when using the Data Observatory functions in SQL queries:
-
It is discouraged to use the SELECT operation with the Data Observatory functions in your map layers. The results may be visible, but CARTO may not support dynamic rendering of the Data Observatory in the future, so your visualizations may break
The Data Observatory is recommended to be used with INSERT or UPDATE operations, for applying analyzed measures and boundaries data to your tables. While SELECT (retrieve) is standard for SQL API requests, be mindful of quota consumption and use INSERT (to insert a new record) or UPDATE (to update an existing record), for best practices.
Exception: [Discovery Functions]({{ site.dataobservatory_docs }}/guides/overview/#discovery-functions) are the exception. You can use SELECT as these functions are not actually retrieving data, they are retrieving ids that you can use for other functions.
-
You can reduce storage space for unneeded geometries and optimize query optimizations by applying the PostGIS
ST_Simplifyfunction. For example, you can simplify thethe_geomfor a large table of polygons and reduce the size of them for quicker rendering. For other tips, see the most commonly used PostGIS functions that you can apply with CARTO -
Only point or polygon geometries are supported for OBS functions. If you attempt to apply Measures or Boundary results to line geometries, an error appears
-
The Data Observatory is optimal for modifying existing tables with analytical results, not for building new tables of data
Exception: Exceptions apply for the following boundary functions, since they were designed to return multiple responses of geographical identifiers, as opposed to a single geometry. Create an empty dataset and build a new dataset from a SQL query, using any one of these boundary functions.
- [
OBS_GetBoundariesByGeometry(geom geometry, geometry_id text)]({{ site.dataobservatory_docs }}/reference/#boundary-functions#obsgetboundariesbygeometrygeom-geometry-geometryid-text) - [
OBS_GetPointsByGeometry(polygon geometry, geometry_id text)]({{ site.dataobservatory_docs }}/reference/#boundary-functions#obsgetpointsbygeometrypolygon-geometry-geometryid-text) - [
OBS_GetBoundariesByPointAndRadius(point geometry, radius numeric, boundary_id text]({{ site.dataobservatory_docs }}/reference/#boundary-functions#obsgetboundariesbypointandradiuspoint-geometry-radius-numeric-boundaryid-text) - [
OBS_GetPointsByPointAndRadius(point geometry, radius numeric, boundary_id text]({{ site.dataobservatory_docs }}/reference/#boundary-functions#obsgetpointsbypointandradiuspoint-geometry-radius-numeric-boundaryid-text)
- [
-
For optimal performance, each SQL request should not exceed 100 rows. As an alternative, you can use a SQL Batch Query for queries with long-running CPU processing times
Examples
View our CARTO Blogs for examples that highlight the benefits of using the Data Observatory.