It was not clear to me what the difference was between a mapnik layer and a cartodb layer until I read the comments in the Mapconfig spec! Let's save some users the extra step :)
31 KiB
Maps API
The CartoDB Maps API allows you to generate maps based on data hosted in your CartoDB account and you can apply custom SQL and CartoCSS to the data. The API generates a XYZ-based URL to fetch Web Mercator projected tiles using web clients such as Leaflet, Google Maps, or OpenLayers.
You can create two types of maps with the Maps API:
-
Anonymous maps
You can create maps using your CartoDB public data. Any client can change the read-only SQL and CartoCSS parameters that generate the map tiles. These maps can be created from a JavaScript application alone and no authenticated calls are needed. See [this CartoDB.js example]({{ '/cartodb-platform/cartodb-js.html' | prepend: site.baseurl }}). -
Named maps
There are also maps that have access to your private data. These maps require an owner to setup and modify any SQL and CartoCSS parameters and are not modifiable without new setup calls.
Quickstart
Anonymous maps
Here is an example of how to create an anonymous map with JavaScript:
var mapconfig = {
"version": "1.3.1",
"layers": [{
"type": "cartodb",
"options": {
"cartocss_version": "2.1.1",
"cartocss": "#layer { polygon-fill: #FFF; }",
"sql": "select * from european_countries_e"
}
}]
}
$.ajax({
crossOrigin: true,
type: 'POST',
dataType: 'json',
contentType: 'application/json',
url: 'https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map',
data: JSON.stringify(mapconfig),
success: function(data) {
var templateUrl = 'https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/' + data.layergroupid + '/{z}/{x}/{y}.png'
console.log(templateUrl);
}
})
Named maps
Let's create a named map using some private tables in a CartoDB account. The following map config sets up a map of European countries that have a white fill color:
{
"version": "0.0.1",
"name": "test",
"auth": {
"method": "open"
},
"layergroup": {
"layers": [{
"type": "mapnik",
"options": {
"cartocss_version": "2.1.1",
"cartocss": "#layer { polygon-fill: #FFF; }",
"sql": "select * from european_countries_e"
}
}]
}
}
The map config needs to be sent to CartoDB's Map API using an authenticated call. Here we will use a command line tool called curl. For more info about this tool, see this blog post, or type man curl in bash. Using curl, and storing the config from above in a file mapconfig.json, the call would look like:
To get the URL to fetch the tiles you need to instantiate the map, where template_id is the template name from the previous response.
The response will return JSON with properties for the layergroupid, the timestamp (last_updated) of the last data modification and some key/value pairs with metadata for the layers.
Note: all layers in metadata will always have a type string and a meta dictionary with the key/value pairs.
Here is an example response:
{
"layergroupid": "c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0",
"last_updated": "1970-01-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"metadata": {
"layers": [
{
"type": "mapnik",
"meta": {}
}
]
}
}
You can use the layergroupid to instantiate a URL template for accessing tiles on the client. Here we use the layergroupid from the example response above in this URL template:
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/{z}/{x}/{y}.png
General Concepts
The following concepts are the same for every endpoint in the API except when it's noted explicitly.
Auth
By default, users do not have access to private tables in CartoDB. In order to instantiate a map from private table data an API Key is required. Additionally, to include some endpoints, an API Key must be included (e.g. creating a named map).
To execute an authorized request, api_key=YOURAPIKEY should be added to the request URL. The param can be also passed as POST param. Using HTTPS is mandatory when you are performing requests that include your api_key.
Errors
Errors are reported using standard HTTP codes and extended information encoded in JSON with this format:
{
"errors": [
"access forbidden to table TABLE"
]
}
If you use JSONP, the 200 HTTP code is always returned so the JavaScript client can receive errors from the JSON object.
CORS support
All the endpoints, which might be accessed using a web browser, add CORS headers and allow OPTIONS method.
Anonymous Maps
Anonymous maps allows you to instantiate a map given SQL and CartoCSS. It also allows you to add interaction capabilities using UTF Grid.
Instantiate
Definition
```html POST /api/v1/map ```Params
{
"version": "1.3.0",
"layers": [{
"type": "mapnik",
"options": {
"cartocss_version": "2.1.1",
"cartocss": "#layer { polygon-fill: #FFF; }",
"sql": "select * from european_countries_e",
"interactivity": ["cartodb_id", "iso3"]
}
}]
}
Should be a Mapconfig.
Response
The response includes:
-
layergroupid
The ID for that map, used to compose the URL for the tiles. The final URL is:https://{account}.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/:layergroupid/{z}/{x}/{y}.png -
updated_at
The ISO date of the last time the data involved in the query was updated. -
metadata Includes information about the layers.
-
cdn_url
URLs to fetch the data using the best CDN for your zone.
Example
Retrieve resources from the layergroup
Mapnik tiles can be accessed using:
These tiles will get just the mapnik layers. To get individual layers see next section.
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/{z}/{x}/{y}.png
Individual layers
The MapConfig specification holds the layers definition in a 0-based index. Layers can be requested individually in different formats depending on the layer type.
Individual layers can be accessed using that 0-based index. For UTF grid tiles:
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/:layer/{z}/{x}/{y}.grid.json
In this case, :layer as 0 returns the UTF grid tiles/attributes for layer 0, the only layer in the example MapConfig.
If the MapConfig had a Torque layer at index 1 it could be possible to request it with:
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/1/{z}/{x}/{y}.torque.json
Attributes defined in attributes section:
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/:layer/attributes/:feature_id
Which returns JSON with the attributes defined, like:
{ "c": 1, "d": 2 }
Blending and layer selection
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/:layer_filter/{z}/{x}/{y}.png
Note: currently format is limited to png.
:layer_filter can be used to select some layers to be rendered together. :layer_filter supports two formats:
allalias
Using all as :layer_filter will blend all layers in the layergroup
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/all/{z}/{x}/{y}.png
- Filter by layer index
A list of comma separated layer indexes can be used to just render a subset of layers. For example 0,3,4 will filter and blend layers with indexes 0, 3, and 4.
https://documentation.cartodb.com/api/v1/map/c01a54877c62831bb51720263f91fb33:0/0,3,4/{z}/{x}/{y}.png
Some notes about filtering:
- Invalid index values or out of bounds indexes will end in
Invalid layer filteringerrors. - Once a mapnik layer is selected, all mapnik layers will get blended. As this may change in the future it is recommended to always select all mapnik layers if you want to select at least one so you will get a consistent behavior in the future.
- Ordering is not considered. So right now filtering layers 0,3,4 is the very same thing as filtering 3,4,0. As this may change in the future it is recommended to always select the layers in ascending order so you will get a consistent behavior in the future.
Create JSONP
The JSONP endpoint is provided in order to allow web browsers access which don't support CORS.
Definition
```bash GET /api/v1/map?callback=method ```Params
-
config Encoded JSON with the params for creating named maps (the variables defined in the template).
-
lmza
This attribute contains the same as config but LZMA compressed. It cannot be used at the same time asconfig. -
callback
JSON callback name.
Example
Remove
Anonymous maps cannot be removed by an API call. They will expire after about five minutes but sometimes longer. If an anonymous map expires and tiles are requested from it, an error will be raised. This could happen if a user leaves a map open and after time, returns to the map and attempts to interact with it in a way that requires new tiles (e.g. zoom). The client will need to go through the steps of creating the map again to fix the problem.
Named Maps
Named maps are essentially the same as anonymous maps except the MapConfig is stored on the server and the map is given a unique name. Two other big differences are: you can create named maps from private data and that users without an API Key can see them even though they are from that private data.
The main two differences compared to anonymous maps are:
-
auth layer
This allows you to control who is able to see the map based on a token auth -
templates
Since the MapConfig is static it can contain some variables so the client can modify the map's appearance using those variables.
Template maps are persistent with no preset expiration. They can only be created or deleted by a CartoDB user with a valid API_KEY (see auth section).
Create
Definition
```html POST /api/v1/map/named ```Params
- api_key is required
Arguments
- name: There can be at most one template with the same name for any user. Valid names start with a letter or a number, and only contain letters, numbers, dashes (-) or underscores (_).
- auth:
- method
"token"or"open"(the default if no"method"is given). - valid_tokens when
"method"is set to"token", the values listed here allow you to instantiate the named map.
- method
- placeholders: Variables not listed here are not substituted. Variables not provided at instantiation time trigger an error. A default is required for optional variables. Type specification is used for quoting, to avoid injections see template format section below.
- layergroup: the layer list definition. This is the MapConfig explained in anonymous maps. See MapConfig documentation for more info.
- view (optional): extra keys to specify the compelling area for the map. It can be used to have a static preview of a named map without having to instantiate it. It is possible to specify it with
center+zoomor with a bounding boxbbox. Center+zoom takes precedence over bounding box.- zoom The zoom level to use
- center
- lng The longitude to use for the center
- lat The latitude to use for the center
- bounds
- west: LowerCorner longitude for the bounding box, in decimal degrees (aka most western)
- south: LowerCorner latitude for the bounding box, in decimal degrees (aka most southern)
- east: UpperCorner longitude for the bounding box, in decimal degrees (aka most eastern)
- north: UpperCorner latitude for the bounding box, in decimal degrees (aka most northern)
Template Format
A templated layergroup allows the use of placeholders in the "cartocss" and "sql" elements of the "option" object in any "layer" of a layergroup configuration
Valid placeholder names start with a letter and can only contain letters, numbers, or underscores. They have to be written between the <%= and %> strings in order to be replaced.
Example
<%= my_color %>
The set of supported placeholders for a template will need to be explicitly defined with a specific type and default value for each.
Placeholder Types
The placeholder type will determine the kind of escaping for the associated value. Supported types are:
- sql_literal internal single-quotes will be sql-escaped
- sql_ident internal double-quotes will be sql-escaped
- number can only contain numerical representation
- css_color can only contain color names or hex-values
Placeholder default values will be used whenever new values are not provided as options at the time of creation on the client. They can also be used to test the template by creating a default version with new options provided.
When using templates, be very careful about your selections as they can give broad access to your data if they are defined losely.
Instantiate
Instantiating a map allows you to get the information needed to fetch tiles. That temporal map is an anonymous map.
Definition
```html POST /api/v1/map/named/:template_name ```Param
- auth_token optional, but required when
"method"is set to"token"
// params.json
{
"color": "#ff0000",
"cartodb_id": 3
}
The fields you pass as params.json depend on the variables allowed by the named map. If there are variables missing it will raise an error (HTTP 400)
- auth_token optional if the named map needs auth
Example
You can initialize a template map by passing all of the required parameters in a POST to /api/v1/map/named/:template_name.
Valid credentials will be needed if required by the template.
You can then use the layergroupid for fetching tiles and grids as you would normally (see anonymous map section). However you'll need to show the auth_token, if required by the template.
Using JSONP
There is also a special endpoint to be able to initialize a map using JSONP (for old browsers).
Definition
```bash GET /api/v1/map/named/:template_name/jsonp ```Params
- auth_token optional, but required when
"method"is set to"token" - config Encoded JSON with the params for creating named maps (the variables defined in the template)
- lmza This attribute contains the same as config but LZMA compressed. It cannot be used at the same time than
config. - callback: JSON callback name
This takes the callback function (required), auth_token if the template needs auth, and config which is the variable for the template (in cases where it has variables).
url += "config=" + encodeURIComponent(
JSON.stringify({ color: 'red' });
The response is in this format:
callback({
layergroupid: "dev@744bd0ed9b047f953fae673d56a47b4d:1390844463021.1401",
last_updated: "2014-01-27T17:41:03.021Z"
})
Update
Definition
```bash PUT /api/v1/map/named/:template_name ```Params
- api_key is required
Response
Same as updating a map.
Other Info
Updating a named map removes all the named map instances so they need to be initialized again.
Example
If any template has the same name, it will be updated.
If a template with the same name does NOT exist, a 400 HTTP response is generated with an error in this format:
{
"errors" : ["error string here"]
}
Delete
Delete the specified template map from the server and it disables any previously initialized versions of the map.
Definition
```bash DELETE /api/v1/map/named/:template_name ```Params
- api_key is required
Example
On success, a 204 (No Content) response will be issued. Otherwise a 4xx response with an error will be returned.
Listing Available Templates
This allows you to get a list of all available templates.
Definition
```bash GET /api/v1/map/named/ ```Params
- api_key is required
Example
Getting a Specific Template
This gets the definition of a template.
Definition
```bash GET /api/v1/map/named/:template_name ```Params
- api_key is required
Example
Use with CartoDB.js
Named maps can be used with CartoDB.js by specifying a named map in a layer source as follows. Named maps are treated almost the same as other layer source types in most other ways.
var layerSource = {
user_name: '{your_user_name}',
type: 'namedmap',
named_map: {
name: '{template_name}',
layers: [{
layer_name: "layer1",
interactivity: "column1, column2, ..."
}]
}
}
cartodb.createLayer('map_dom_id',layerSource)
.addTo(map_object);
CartoDB.js has methods for accessing your named maps.
- layer.setParams() allows you to change the template variables (in the placeholders object) via JavaScript
- layer.setAuthToken() allows you to set the auth tokens to create the layer
Static Maps API
The Static Maps API can be initiated using both named and anonymous maps using the 'layergroupid' token. The API can be used to create static images of parts of maps and thumbnails for use in web design, graphic design, print, field work, and many other applications that require standard image formats.
Maps API endpoints
Begin by instantiating either a named or anonymous map using the layergroupid token as demonstrated in the Maps API documentation above. The layergroupid token calls to the map and allows for parameters in the definition to generate static images.
Zoom + center
Definition
```bash GET /api/v1/map/static/center/:token/:z/:lat/:lng/:width/:height.:format ```Params
- :token: the layergroupid token from the map instantiation
- :z: the zoom level of the map
- :lat: the latitude for the center of the map
- :lng: the longitude for the center of the map
- :width: the width in pixels for the output image
- :height: the height in pixels for the output image
- :format: the format for the image, supported types:
png,jpg- jpg will have a default quality of 85.
Bounding Box
Definition
```bash GET /api/v1/map/static/bbox/:token/:bbox/:width/:height.:format` ```Params
- :token: the layergroupid token from the map instantiation
- :bbox: the bounding box in WGS 84 (EPSG:4326), comma separated values for:
- LowerCorner longitude, in decimal degrees (aka most western)
- LowerCorner latitude, in decimal degrees (aka most southern)
- UpperCorner longitude, in decimal degrees (aka most eastern)
- UpperCorner latitude, in decimal degrees (aka most northern)
- :width: the width in pixels for the output image
- :height: the height in pixels for the output image
- :format: the format for the image, supported types:
png,jpg- jpg will have a default quality of 85.
Note: you can see this endpoint as:
GET /api/v1/map/static/bbox/:token/:west,:south,:east,:north/:width/:height.:format`
Named map
Definition
```bash GET /api/v1/map/static/named/:name/:width/:height.:format ```Params
- :name: the name of the named map
- :width: the width in pixels for the output image
- :height: the height in pixels for the output image
- :format: the format for the image, supported types:
png,jpg- jpg will have a default quality of 85.
A named maps static image will get its constraints from the view in the template, if view is not present it will estimate the extent based on the involved tables otherwise it fallback to "zoom": 1, "lng": 0 and "lat": 0.
####Layers
The Static Maps API allows for multiple layers of incorporation into the MapConfig to allow for maximum versatility in creating a static map. The examples below were used to generate the static image example in the next section, and appear in the specific order designated.
Basemaps
{
"type": "http",
"options": {
"urlTemplate": "http://{s}.basemaps.cartocdn.com/dark_nolabels/{z}/{x}/{y}.png",
"subdomains": [
"a",
"b",
"c"
]
}
},
By manipulating the "urlTemplate" custom basemaps can be used in generating static images. Supported map types for the Static Maps API are:
'http://{s}.basemaps.cartocdn.com/dark_all/{z}/{x}/{y}.png',
'http://{s}.basemaps.cartocdn.com/dark_nolabels/{z}/{x}/{y}.png',
'http://{s}.basemaps.cartocdn.com/light_all/{z}/{x}/{y}.png',
'http://{s}.basemaps.cartocdn.com/light_nolabels/{z}/{x}/{y}.png',
Mapnik
{
"type": "mapnik",
"options": {
"sql": "select null::geometry the_geom_webmercator",
"cartocss": "#layer {\n\tpolygon-fill: #FF3300;\n\tpolygon-opacity: 0;\n\tline-color: #333;\n\tline-width: 0;\n\tline-opacity: 0;\n}",
"cartocss_version": "2.2.0"
}
},
CartoDB
As described in the Mapconfig documentation, a "cartodb" type layer is now just an alias to a "mapnik" type layer as above, intended for backwards compatibility.
{
"type": "cartodb",
"options": {
"sql": "select * from park",
"cartocss": "/** simple visualization */\n\n#park{\n polygon-fill: #229A00;\n polygon-opacity: 0.7;\n line-color: #FFF;\n line-width: 0;\n line-opacity: 1;\n}",
"cartocss_version": "2.1.1"
}
},
Additionally, static images from Torque maps and other map layers can be used together to generate highly customizable and versatile static maps.
Caching
It is important to note that generated images are cached from the live data referenced with the layergroupid token on the specified CartoDB account. This means that if the data changes, the cached image will also change. When linking dynamically, it is important to take into consideration the state of the data and longevity of the static image to avoid broken images or changes in how the image is displayed. To obtain a static snapshot of the map as it is today and preserve the image long-term regardless of changes in data, the image must be saved and stored locally.
Limits
- While images can encompass an entirety of a map, the default limit for pixel range is 8192 x 8192.
- Image resolution by default is set to 72 DPI
- JPEG quality by default is 85%
- Timeout limits for generating static maps are the same across the CartoDB Editor and Platform. It is important to ensure timely processing of queries.
Examples
After instantiating a map from a CartoDB account:
Response
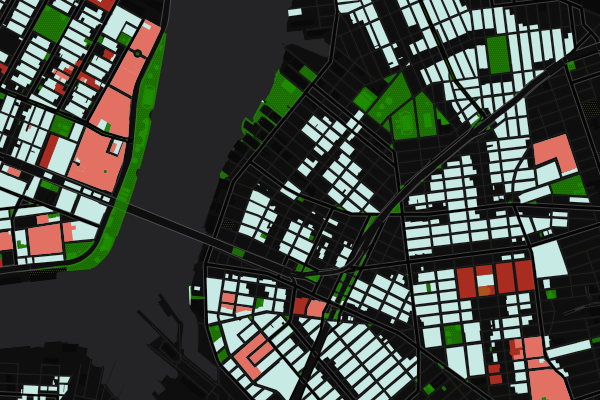
MapConfig
For this map, the multiple layers, order, and stylings are defined by the MapConfig.
{
"version": "1.3.0",
"layers": [
{
"type": "http",
"options": {
"urlTemplate": "http://{s}.basemaps.cartocdn.com/dark_nolabels/{z}/{x}/{y}.png",
"subdomains": [
"a",
"b",
"c"
]
}
},
{
"type": "mapnik",
"options": {
"sql": "select null::geometry the_geom_webmercator",
"cartocss": "#layer {\n\tpolygon-fill: #FF3300;\n\tpolygon-opacity: 0;\n\tline-color: #333;\n\tline-width: 0;\n\tline-opacity: 0;\n}",
"cartocss_version": "2.2.0"
}
},
{
"type": "cartodb",
"options": {
"sql": "select * from park",
"cartocss": "/** simple visualization */\n\n#park{\n polygon-fill: #229A00;\n polygon-opacity: 0.7;\n line-color: #FFF;\n line-width: 0;\n line-opacity: 1;\n}",
"cartocss_version": "2.1.1"
}
},
{
"type": "cartodb",
"options": {
"sql": "select * from residential_zoning_2009",
"cartocss": "/** simple visualization */\n\n#residential_zoning_2009{\n polygon-fill: #c7eae5;\n polygon-opacity: 1;\n line-color: #FFF;\n line-width: 0.2;\n line-opacity: 0.5;\n}",
"cartocss_version": "2.1.1"
}
},
{
"type": "cartodb",
"options": {
"sql": "select * from nycha_developments_july2011",
"cartocss": "/** simple visualization */\n\n#nycha_developments_july2011{\n polygon-fill: #ef3b2c;\n polygon-opacity: 0.7;\n line-color: #FFF;\n line-width: 0;\n line-opacity: 1;\n}",
"cartocss_version": "2.1.1"
}
}
]
}