The etherpad component's nginx configuration needs to know the request scheme in order to set some variables that influence whether the 'Secure' flag is set on cookies. Right now it directly uses the $scheme variable, but this variable does not get set to the expected value if nginx is behind a reverse-proxy where the proxy handles TLS termination. Adjust the etherpad nginx config to use a variable with a different name $real_scheme, which can be set in the nginx server block to match the configuration of the nginx listeners. This variable is set to the value of $scheme in the default /etc/sites-available/bigbluebutton file. The bbb-install.sh script will be updated to set this variable in the configurations it writes. People using other installation scripts will need to add this variable to their nginx configuration file, or etherpad might not operate correctly. |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| packages-template | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| bbb-ci.png | ||
| change_detection.sh | ||
| deb-helper.sh | ||
| get_external_dependencies.sh | ||
| opts-global.sh | ||
| package-names.inc.sh | ||
| push_packages.sh | ||
| README.md | ||
| setup-inside-docker.sh | ||
| setup.sh | ||
build
build scripts for packaging bigbluebutton.
This directory contains scripts for the new open-source Gitlab-CI based build system, which shall replace the legacy non-public Jenkins based process. The build scripts in packages-template have been adapted from the old system, and still have room for improvement / cleanup.
build locally
You can build packages locally. Docker is required to be installed on your machine.
First, get the external dependencies (this can be migrated to git submodules once the legacy CI system has been retired):
./build/get_external_dependencies.sh
For example, to build the bbb-html5 package, run the following command from the repository's root directory.
./build/setup.sh bbb-html5
The package will be put into the artifacts/ subdirectory.
Note that this will pull in the required Docker image from a remote server. If you want to build the container yourself, get the Dockerfile from the repo, build it locally and change the image url in .gitlab-ci.yml to the locally built one.
build using CI
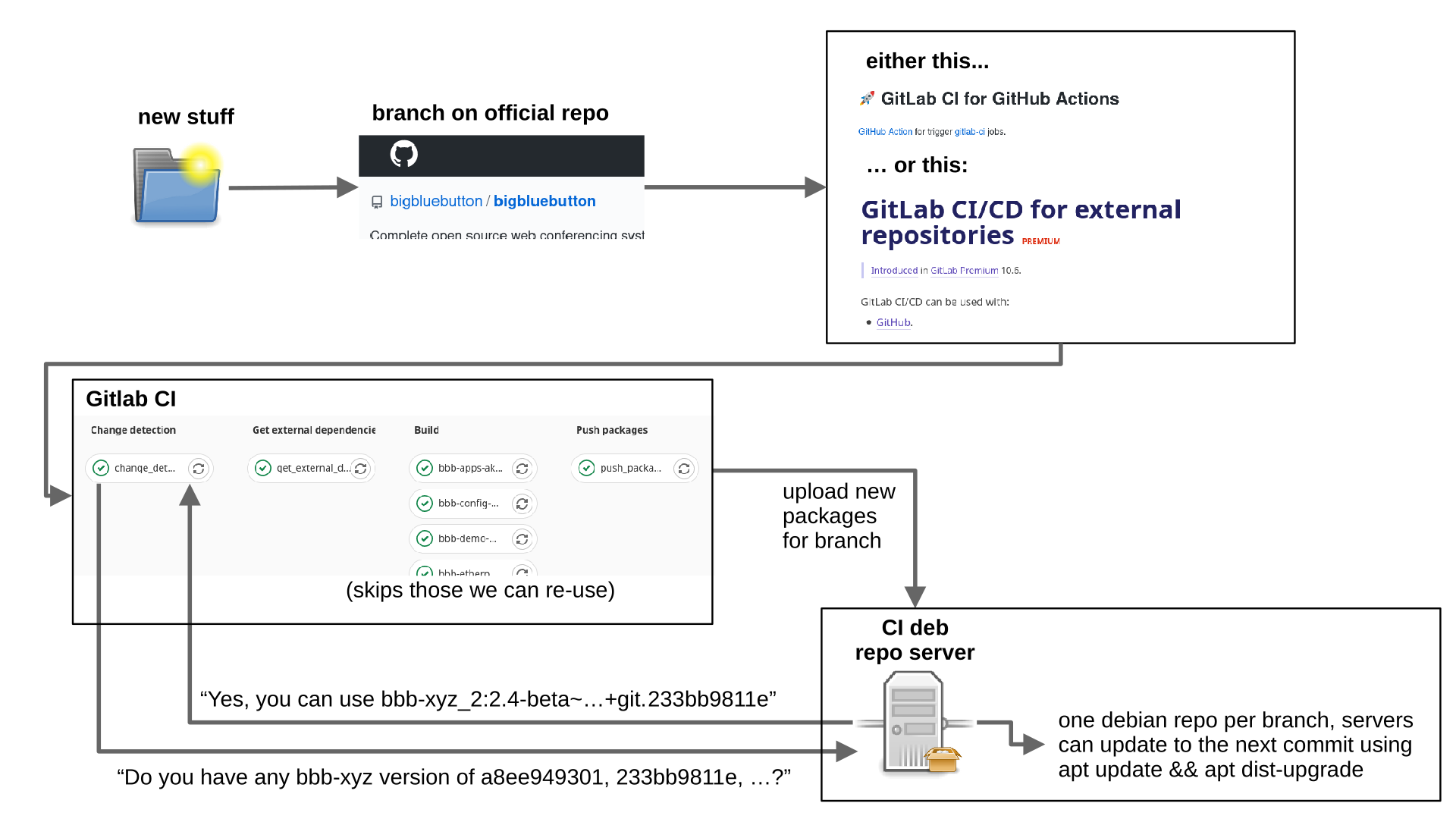
The CI is defined by the file .gitlab-ci.yml in the root directory of this repo.
In CI, the build process is done in four stages:
- The first stage determines the last commit that changed each package, and all commits since that made no change to the package. The debian repository server is then queried, to see whether a package is already available for any of those commits. If yes, the package version is written to a file called
packages-to-skip.txt. - The second steps pulls in external dependencies. This could be later changed to use git submodules. As of now, that would break the old CI, therefore this step exists.
- Debian packages are built in parallel for each component. Packages listed in
packages-to-skip.txtare not build (see stage 1). Abigbluebuttonmeta-package is also created. This package depends on the exact versions of the other core packages, e.g. either packages with the same commit hash (for those that have been built), or the respective version listed inpackages-to-skip.txt. - Packages are uploaded to the debian repository server. The endpoint on the repo server also receives the branch name, and generates/updates that branch's repository with all relevant (uploaded and reused) packages.
The repo server software can be found at https://gitlab.senfcall.de/senfcall-public/ci-repo-upload .